This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS
Parkes Weber syndrome
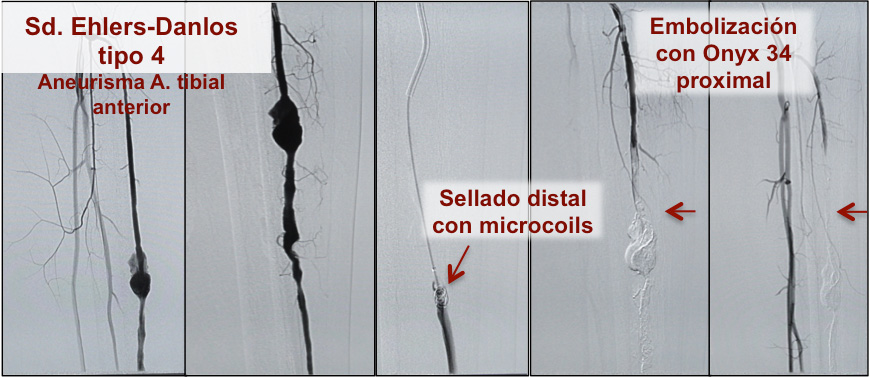
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Cava Agenesis diagnosis
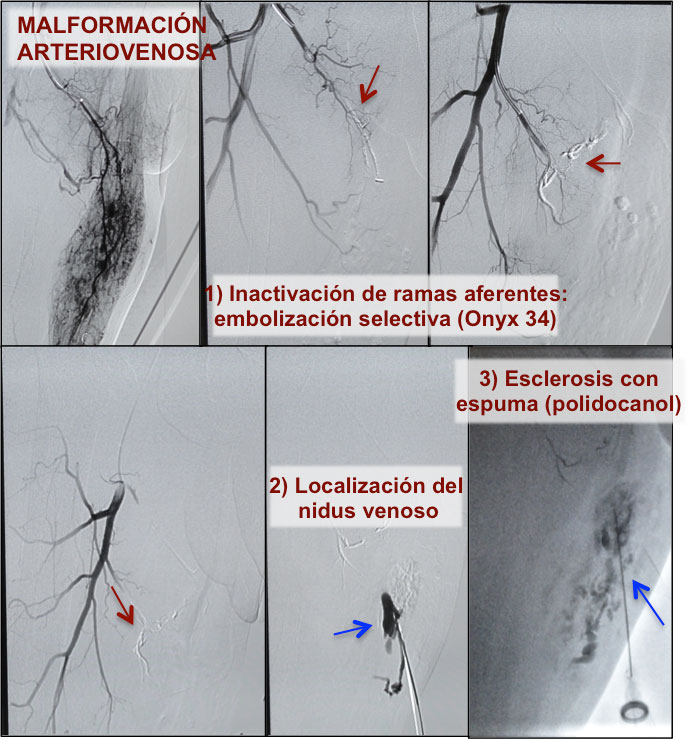
Arteriovenous malformations treatment
DESCRIPTION
What is an Arteriovenous Malformation?
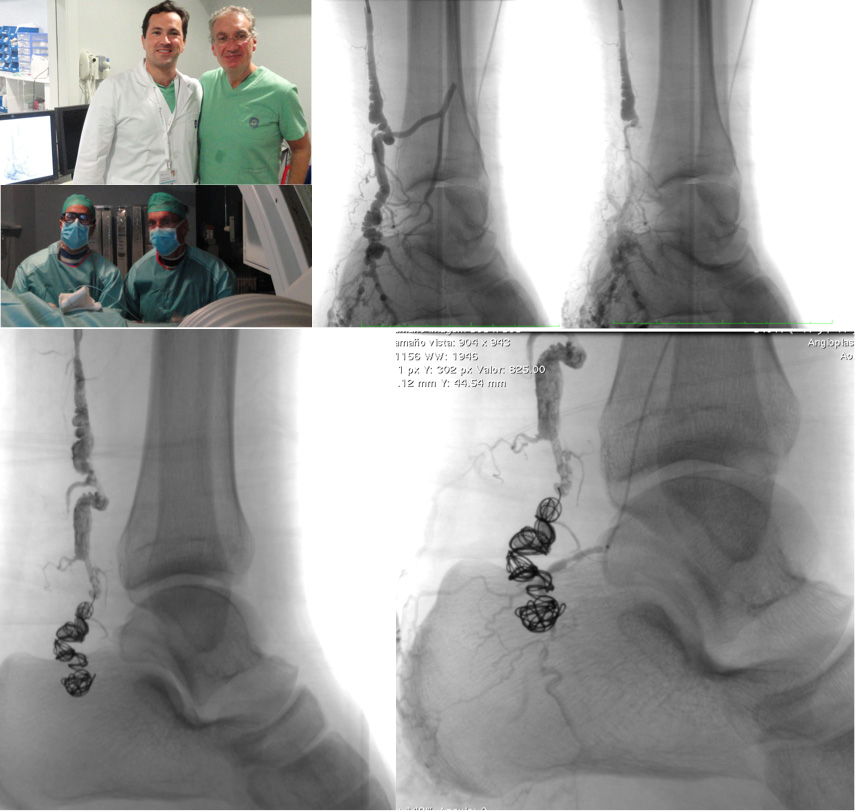
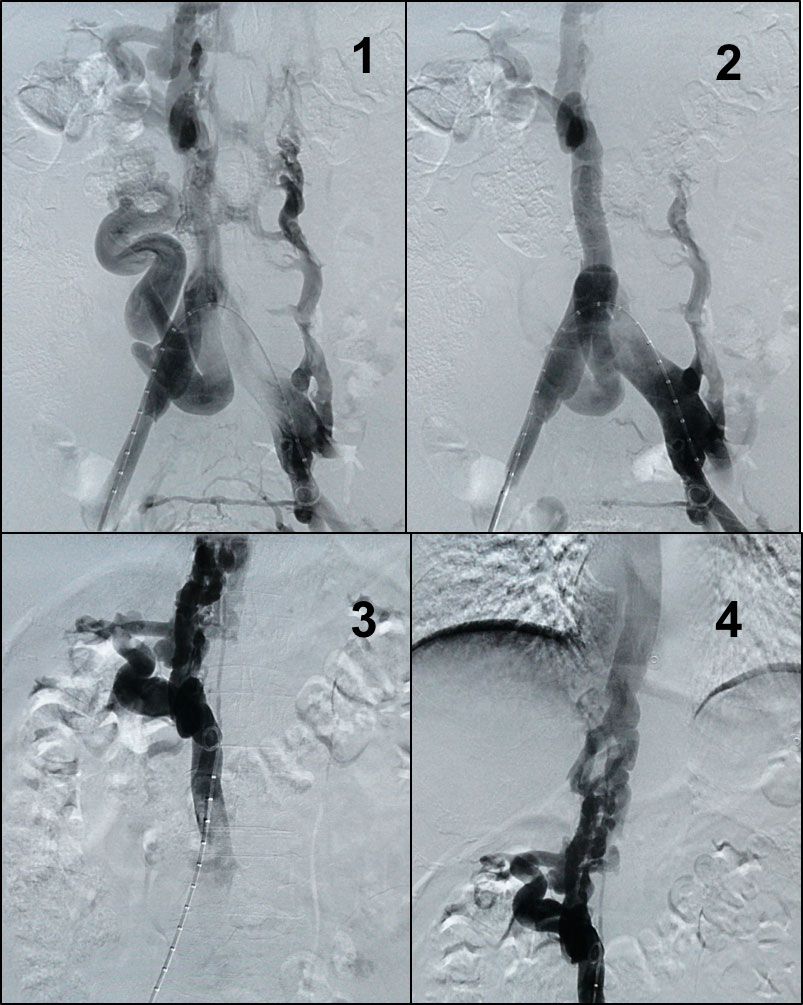
It is a vascular malformation where pathological communication exists between arterial and venous vessels, without any capillary territory mediating between both. There are multiple classifications of vascular malformations and of arteriovenous malformations, but perhaps the greatest significance regarding treatment is to distinguish the high flow or the low flow ones. This group of diseases require highly accurate diagnosis, planning at different stages sometimes and as in everything related to vascular pathology, performing both surgical and endovascular treatments independently.
In this synopsis we can place for example Parkes-Weber or Klippel Trenaunay syndromes, or intramuscular malformations, and a long list of others. Even very complex aneurysmal diseases such as the ones produced by Ehlers-Danlos syndrome may lead to fistulas from rupture of peripheral aneurysms, cirsoid aneurysms, aberrant.
How are they diagnosed and treated?
Ultrasound and tests such as CT and resonance may give us an important approach, although maximum accuracy is crucial in most of the occasions, such as the one provided by phlebography or selective arteriography.
The current first choice treatment is nucleus malformations exclusion (“nidus”) by embolisation with coils, vascular plugs, polyvinyl particles, Onyx, etc. And then polidocanol foam may be applied, resection surgery, and many others, which the Angiologist and Vascular Surgeon will perfectly define according to each type of syndrome or specific malformation.